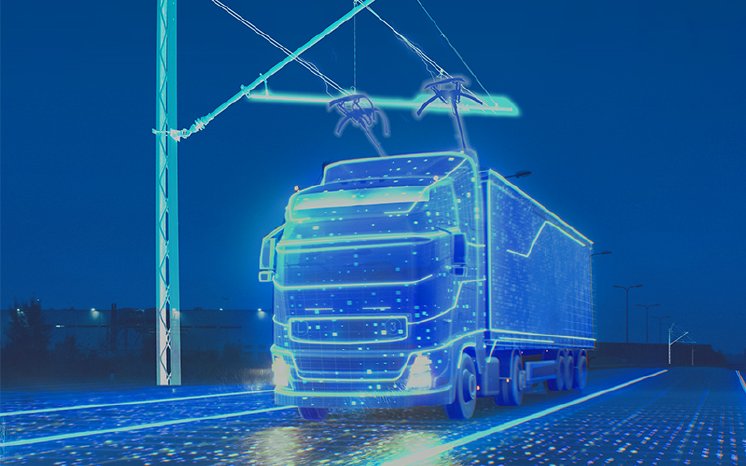
The e-mobility age challenge is increasing charging capabilities for speedier, more efficient, and more convenient journeys. With this in mind, the company has developed this new megawatt charging concept. Applications to secure these patents have been filed.
With the new megawatt charging infrastructure, vehicles are flexibly recharged via the overhead catenary system on any highway. A significant difference from conventional continuous overhead line concepts is that the new concept consists of short megawatt charging sections. Indeed, as the name implies, vehicles can operate on battery power independently of these sections at any time. The overhead charging is implemented via external DC/DC chargers, which transfer the energy directly to the vehicle while driving along the highway. With the help of over-the-air pre-registration of the respective vehicle system, vehicles are optimally prepared for the charging process before reaching the charging section. This step ensures that the maximum possible battery charging energy will be available in the corresponding overhead line section. Therefore, the best possible use of the overhead line is achieved.
The overhead catenary voltage depends on the state of charge of the vehicle battery (SOC), which reaches from 600 V up to 1,250 V. The length of the overhead charging section is variable and depends on the required charging energy per vehicle and the number of cars to be charged. According to the latest calculations of the battery team, the charging power can reach up to 3,000 A or 3.75 MW. All vehicles moving within a catenary section can be charged and simultaneously use electrical power for traction. At the same time, vehicles can only use electric power for driving, whereby the e-motor power of about 200-500 kW provides pure EV operation in all road and weather conditions. Multiple charging modes allow individual reactions to different traffic volumes.
Current estimations suggest that charging times for commercial vehicles and trucks on highways can be reduced by up to 90 %.
The concept offers a second charging option with a standardized, compatible CCS or MCS charging plug. This means that vehicles can also be charged, for example, in charging parks at service stations and logistics centers or customers' logistics areas.
By taking this step, the company is sending a clear signal: The cost-efficiency improvement of electric mobility is also essential for commercial transport vehicles such as delivery services and commercial applications. In addition to human-operated vehicles, this flexible and consistently available charging alternative holds great potential for autonomous operations. Vehicles without drivers are not required to comply with the legally binding driving and rest periods, making 100 % permanent operations a reality.
"We challenge the status quo by rethinking concepts to achieve greater economic efficiency, innovation, value, and sustainability. In doing so, our resources and energy focus on technologies with a real future, where every evaluation and decision is based on strong test results, multi-stage simulations, and valuable experiences from real customer projects," replies Gerold Sluka when asked about the motivation behind these patents.