Ethylene oxide is widely used to sterilize materials and instruments used in surgery and for medical devices but is not permitted to be used in foodstuff in Europe. Its biocidal usage was banned in Europe due to toxicity risks, and it is not approved as an active substance in plant protection products in the EU.
Since September 2020, the RASFF European system (Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed) has reported the entry of multiple foodstuffs contaminated with ethylene oxide into European countries.
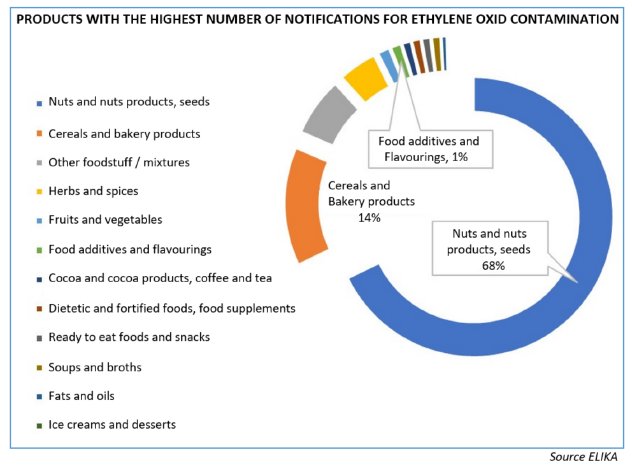
Alerts were initially reported after detections at sesame seeds in September 2020, and after an increase of controls agreed by state members at several subsequent meetings, a large number of non-compliances with the MRLs for ethylene oxide, for products of origins other than India, and other than sesame seeds, as well as for organic products, were recorded.
During June and July 2021 different food safety agencies from EU member states, issued press releases sharing their concern and reporting a list of over 7,000 products that contained high levels of this pesticide, which is considered carcinogenic, mutagenic and toxic to reproduction, and is banned for use in Europe. In addition, its presence has been linked to two food additives, E410 (carob bean gum) and E412 (guar gum), although it has since been further stated that only some batches of these additives were contaminated with ethylene oxide.
Given this complex situation, and in order to help the food industry and protect consumers,L.A.B. has developed and tuned a method of analysis for ethylene oxide in food, in accordance with its residue definition according to Reg. (EC) 396/2005, which defines it as the sum of ethylene oxide and 2-chloro-ethanol (a related product) expressed as ethylene oxide.
For further information, please do not hesitate to contact the L.A.B. | Bioclinical Analytical Laboratory team.