What is the Definition of a Digital Twin?
Simply put, a digital twin is a virtual representation of a product or process. This means that you can create your production line virtually before building it in the real world to see how it will work and what issues may arise.
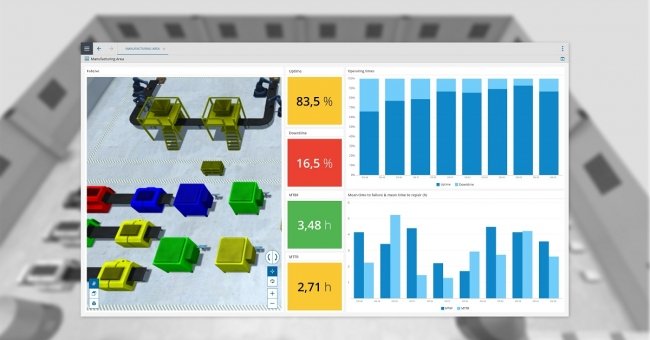
Once the production line is up and running in the real world sensors on the line can feed data to its digital twin. The digital twin can then be used to analyze how well the line is running and make predictions, based on how it’s run in the past, on how it’ll run in the future.
The results of the analysis can be turned into actions in the real world. For example, oven temperatures could be adjusted on the production line or replacement parts could be requested and maintenance scheduled.
With enough data you can even run scenarios to see how your production line will be affected under different circumstances.
The Benefits of a Digital Twin
Defining a digital twin is easy. Listing all of the benefits takes a bit longer. Below are just a few of the major benefits of using a digital twin of your products, plants and processes:
- Faster New Product Introduction (NPI): By utilizing a digital twin, you can replicate the planned production process of your new product and game out all the scenarios of what could go wrong before you even start to build your production line. This prevents costly adjustments later on when physical, rather than digital equipment, needs to be adjusted.
- Reduced Downtime: Digital twins of your equipment can predict how long that equipment is expected to run for, based on past data, before it requires maintenance. If the twin is being fed with current data from the real equipment then it can modify its estimate based on its performance deterioration. This predictive maintenance feature allows you to plan maintenance during existing stoppages and avoid breakdowns which will reduce overall downtime.
- Reduced Scrap and Rework Costs: A digital twin of your product can be run through your manufacturing processes to predict where issues may arise. By utilizing data from previous product production runs you can see where similar issues are likely to arise with your next product. The digital twin of a production line doesn't need to live in isolation. By training it with data from other production line processes it becomes better equipped to predict and reduce scrap and rework.
- Predict Gains/Losses of Modifying Production: With enough data on your equipment, processes and products you can calculate whether making adjustments to your manufacturing process are financially viable. If you run that piece of equipment 10% faster will the benefits outweigh the costs of more frequent maintenance? Don't forget, the digital twin doesn't just utilize physical data - one of its biggest benefits is in its ability to integrate financial data, such as the cost of materials and labor.
- Reduced Training Costs: Using augmented reality (AR), live video of equipment on the plant floor is overlaid with information fed from the digital twin. This could include the current status of various components or it could guide an engineer through repair procedures. The use of augmented reality can greatly reduce training requirements, increase overall safety and raise the efficiency of people working on the production line.
- Improved Supply Chain Management: Moving beyond your plant, a digital twin of the supply chain feeding into your manufacturing processes can be tweaked and fine-tuned so that procurement, logistics and delivery can be predicted and optimized. Sharing data with your suppliers will allow you to extend and strengthen the digital thread of your products so you can make the right tactical and strategic decisions with the best information available, reducing costs and supporting your Supply Chain Management (SCM).