As part of the PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) mission, NASA is planning to measure the “color of the oceans” from a satellite scheduled to launch in 2022. The mission will help scientists investigate microscopic ocean organisms that play a significant role in feeding marine life, aerosols, and clouds – and the role all of these plays in the Earth system.
OCI – Ocean Color Instrument
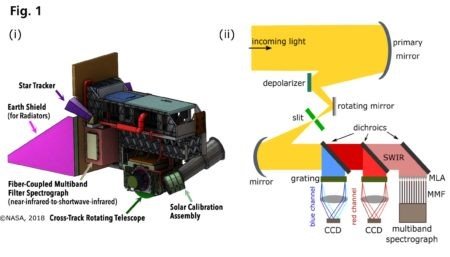
The central instrument of the PACE Satellite is a highly advanced optical spectrometer called the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), that measures properties of light from ocean environments over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum from ultraviolet to short-wavelength Infrared (SWIR). A schematic showing the planned layout and principle of OCI can be seen in Fig. 1(i) and 1(ii) respectively. Its advantage to previous NASA satellite sensors is its hyperspectral capability, i.e. improved spectral resolution of 5 nm when measuring the spectral range between 350-885 nm and large signal to noise ratios (SNRs). Moreover, to retrieve accurate ocean optical properties, OCI can remove unwanted reflectance contributions from the atmosphere (e.g. aerosol reflectance) and ocean surface. This atmospheric correction especially for near-shore regions or turbid waters is performed in the SWIR range where water absorption is few orders of magnitude greater than in the near infrared, ensuring nearly z ero ocean reflectance. The PACE Team at the Goddard Space Flight Center is currently developing the system to meet performance standards from scientists studying the atmosphere, ocean and even land surface. The planned satellite will orbit around earths northern-southern hemispheres at an altitude of 675 km and consists of a cross-track rotating telescope that makes 360 rotations per minute and has a field of view of ± 56.5 °. For every instance in time, the telescope records an array of 1 x 16 spatial pixels also called “science pixels” by NASA where each pixel amounts to a 1 x 1 km geographical area measured at Nadir. Furthermore, to ensure high SNRs by building enough signal for integration, the telescope views the same geographical scene on earth for an extended time by imaging every “science pixel” 16 times, as it rotates. This broadband light signal from oceans (acquired in the form of 16 spatial pixels) is reflected off a primary mirror (an off-axis parabola), depolarized and projected onto a rectangular slit. Thereafter, it is collimated and redirected using dichroic beam splitters to blue and red hyperspectral channels where dispersive gratings separate the individual wavelengths respectively and image them on time delay integration-charged coupled devices (TDI-CCDs). The SWIR bands are analyzed using a remotely located multi-band filter spectrograph that contains a temperature cooled 1 x 16 detector array. To couple light into the detector array, a 1 x 16 bundle of 600 µm core sized multi-mode fiber (MMF) with a numerical aperture of 0.22 is used. This is a superior approach than using 16 individual lens systems to couple incoming light from telescope to the detector array where precise mechanical alignment is cumbersome and prone to errors. For efficient coupling of collimated light into the MMFs, NASA decided to use aspherical micro-lens arrays (MLA) with the requirement of low coupling losses. To minimize polarization dependent losses, both the MM Fs and the MLAs required broadband anti-reflection coating from 0.9 to 2.3 µm. The goal is to be able to couple light over the entire spectrum with an efficiency of 95 percent.
The selection process
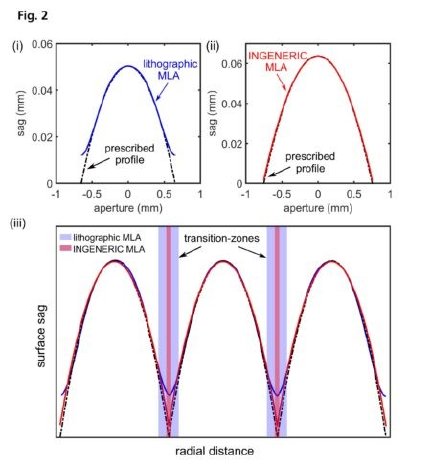
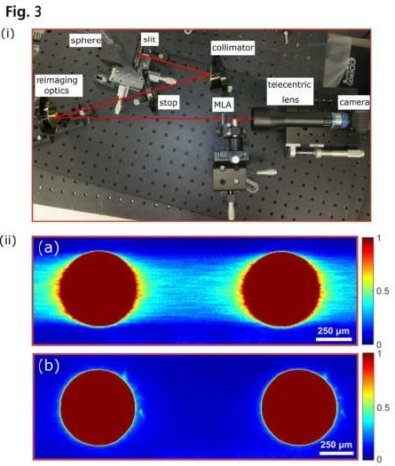
For the initial testing phase, NASA obtained commercially available lithographically produced quartz MLA with a pitch (lens center-to-center distance) of 1.3 mm. To determine the performance of the MLA, the surface profile of individual lenses was measured and compared with the desired lens surface profile where considerable deviations in surface sag profile at the lens edges of the lithographic lens were found (Fig. 2 (i)). During optical simulations with commercial software Zemax, the measured surface sag errors at edges showed an increase in the spherical aberration at the image plane, which has the consequence of decreased coupling efficiency into fibers. Moreover, in the case of an array of aspherical micro-lenses, deviations of surface sag especially at the micro-lens edges can lead to the formation of dead transition zones (flat and shallow interfaces) between consecutive lenslets as shown in Fig.2 (iii). These dead zones were characterized using a laboratory bench-top imaging setup by NASA whose layout can be seen in Fig. 3(i).
Using this setup, white light that passed through a rectangular slit located at the focal plane of the telescope was collimated and redirected to illuminate the MLA. The MLA generated 16 round images of the telescope exit pupil, which were imaged using a telecentric lens on a SWIR camera. The resulting images showed leakage of ‘stray’ light from interfacial areas between the lenslets shown in part (a) of Fig. 3(ii) and can be attributed to presence of optical aberrations. In aspherical MLAs, the presence of spherical aberrations and transition zones has the consequence of reduced optical coupling efficiency of light into optical fibers. In search of MLA where the coupling efficiency could be improved, NASA decided to test MLAs fabricated using a precision molding technique. For the second design phase, NASA tested aspherical MLAs from INGENERIC (Fig. 4) with a pitch of 1.5 mm. For this test phase, NASA increased both the lens radius of curvature and array pitch to compensate for chan ges in instrument layout. At the beginning of the project, to ensure that the quality of the glass and coating meet the requirements, INGENERIC provided NASA with plane glass samples with a special anti-reflection coating optimized for the entire spectrum from 0.9 to 2.3 µm. Subsequent tests confirmed that the transmissivity requirements were met.The next step was to test the accuracy of surface form of produced MLAs and their imaging properties. Using a commercial areal confocal 3D measurement setup (NanoFocus µsurf), the surface profile of the MLA was measured by INGENERIC and compared to the design requirements by NASA. As shown in Fig. 2(ii) a comparison of the two profiles showed an excellent agreement between the design requirements of NASA and the INGENERIC manufactured lens profile. This resulted in the INGENERIC produced MLAs to have transition zones that were almost an order of magnitude smaller than the MLAs produced by lithographic methods! Furthermore, pitch analysis of the INGENERIC MLA showed an exceptional accuracy with pitch errors.