About the SyncroPatch 384
The SyncroPatch 384 is a high throughput automated patch clamp instrument for recording from up to 384 wells simultaneously.
The system comes equipped with temperature control for heated experiments at physiological temperature, or cooled experiments below room temperature. It is highly flexible and easy-to-use and experiments can be performed using different solutions, with or without fluoride and high divalent solutions. The 32-well mode can be used for smaller screening projects and assay development.
About cardiac safety testing
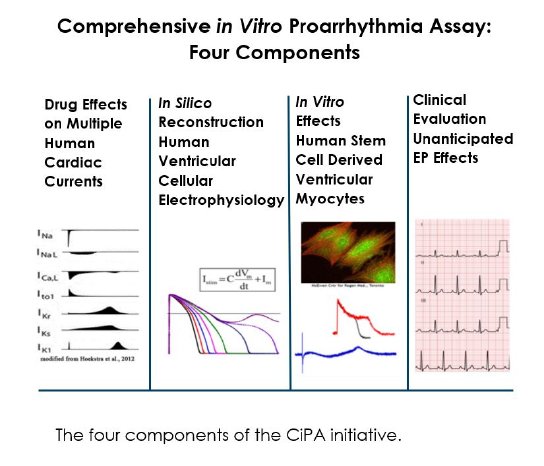
The ICH S7B non-clinical guidance was introduced in November 2005 and required all new drugs to be tested for activity on IKr carried by hERG-expressed in recombinant cell lines using the patch-clamp technique, as blockade of the hERG channel has been attributed to drug-induced long QT syndrome and potentially fatal Torsade de Pointes (TdP). Since the introduction of these guidelines, very few drugs have been withdrawn from the market due to proarrhythmic complications. In 2013 the Comprehensive in vitro Proarrhythmia Assay (CiPA) initiative was started to further improve risk prediction, by accounting for drug block of cardiac ion channels (e.g., NaV1.5 and CaV1.2) that may mitigate the risk of hERG block.
This effort is to ensure that drugs that reach the market are safe, by identifying candidate compounds with the potential to cause potentially fatal arrhythmia, but also to reduce the number of false positives ensuring that potentially useful (and safe) drugs do reach the market.
Chief Operating Officer at Nanion Technologies Inc., Rodolfo Haedo, was thrilled to announce the installation at the FDA saying,
‘Cardiac safety testing of compounds is paramount to ensuring safe compounds reach the market, and typically ion channel data submitted to the FDA are generated by manual patch clamp systems. The SyncroPatch 384 has now been installed at the FDA’s Silver Spring site, and it will be used to evaluate how automated patch clamp data may be used in the regulatory context. Data generated by the SyncroPatch 384 will be compared with those concurrently generated using the manual patch clamp method, and we look forward to this comparison’.
Nanion Technologies GmbH Director of Scientific Affairs and CiPA panel expert,
Dr. Sonja Stölzle-Feix said,
‘The CiPA initiative is an ongoing project aimed at ensuring cardiac safety of new compounds, whilst at the same time making sure that safe drugs don’t fail early on in the pipeline due to hERG block when they are not pro-arrhythmic. Both the FDA and Nanion Technologies, amongst other institutions and companies, have been heavily involved in standardizing experimental protocols for patch clamp experiments. We are looking forward to working with the FDA to ensure efficient transfer of their manual patch clamp assays onto the SyncroPatch 384.’
About the FDA
The Food and Drug Administration is responsible for protecting the public health by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, and medical devices; and by ensuring the safety of our nation's food supply, cosmetics, and products that emit radiation.
FDA also has responsibility for regulating the manufacturing, marketing, and distribution of tobacco products to protect the public health and to reduce tobacco use by minors.
FDA is responsible for advancing the public health by helping to speed innovations that make medical products more effective, safer, and more affordable and by helping the public get the accurate, sciencebased information they need to use medical products and foods to maintain and improve their health.
FDA also plays a significant role in the Nation's counterterrorism capability. FDA fulfills this responsibility by ensuring the security of the food supply and by fostering development of medical products to respond to deliberate and naturally emerging public health threats.