Automation is rightly one of the current trend topics in the business world, as the digitalisation, optimisation and ultimately automation of business processes holds great potential for companies. In this context, the activities of specialised departments are automated, which leads to cost savings, the acceleration of processes and an increase in quality. Relieving employees of routine tasks through automation offers a great opportunity in dealing with the shortage of skilled labour. On the one hand, the workload of staff can be reduced. On the other hand, employee productivity can be increased if they can concentrate on value-adding activities instead of filling their working day with routine tasks.
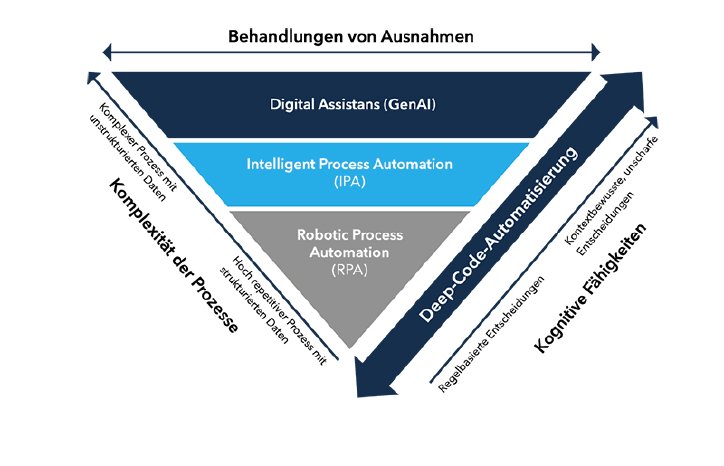
Deep code automation and RPA are presented below.
Deep code automation
Deep code automation describes the classic approach to automation using programming (PowerShell, Python, HTML / CSS and C#, etc.) and scripting. Here, solutions are programmed from scratch and precisely tailored by using existing interfaces and infrastructures.
Individual activities can often be automated in a sensible and cost-saving way using a script. For more complex activities, however, this approach can also involve a high level of development effort. This means that there is little certainty in terms of effort and costs. In addition, maintenance must be ensured after development, which requires a deep technical understanding of the solution. Professional process changes can also entail complex technical changes.
For this reason, this approach should always be carried out with an experienced team in order to limit the aforementioned risks. An experienced team of consultants can significantly limit the risks, e.g. through precise analysis of the process to be automated, modularized development of the code and a well thought-out IT architecture. The transfer of knowledge to internal staff during the course of implementation is also essential in order to minimize future dependence on external support.
The major advantage of this approach is the ability to tailor solutions. As there are hardly any technical limits to the complexity of the developed solution, the requirements of a specialist department or a company can be implemented precisely - regardless of whether they are extensive regulatory requirements or very individual requirements.
RPA - customised automation
A high degree of automation can be achieved for a large proportion of common business processes using simple means. Repetitive activities with defined processes can be automated cost-effectively and very often completely with Robot Process Automation (RPA). If RPA platforms such as UiPath, Power Platform or Automation Anywhere are used, cost-effective "off-the-shelf" automation is possible.
By accessing applications that were previously operated by humans, RPA bots take over rule-based human screen activities. In concrete terms, this means that the RPA robots access existing IT systems via the front end in a similar way to the actions of a human and type, copy, paste, extract or merge. As these platforms place low demands on the IT infrastructure and access existing interfaces or user interfaces, implementation is usually possible quickly and interaction with practically any software is possible.
As a result, surprisingly fast ROIs (return on investment) are regularly achieved in RPA projects. Particularly if the automated process (step) is frequent or involves a high volume of work, this can save a great deal of time. An increase in quality and savings in opportunity costs are also typical results of process automation with RPA.
This type of automation requires significantly less effort than automation through programming. Once the automated process has matured, changes are usually only necessary if a user interface of an application without an interface is changed.
Before automating with RPA, it is essential to take a proper look at the process in question. If it is not mature enough, incompletely defined or even defective, it cannot be optimized by pure automation. Automation is often carried out by a team with exclusively technical skills. Unfortunately, in practice, the repair of the poor process is often neglected before the automation is carried out. We therefore always recommend prior process optimization before implementing RPA.