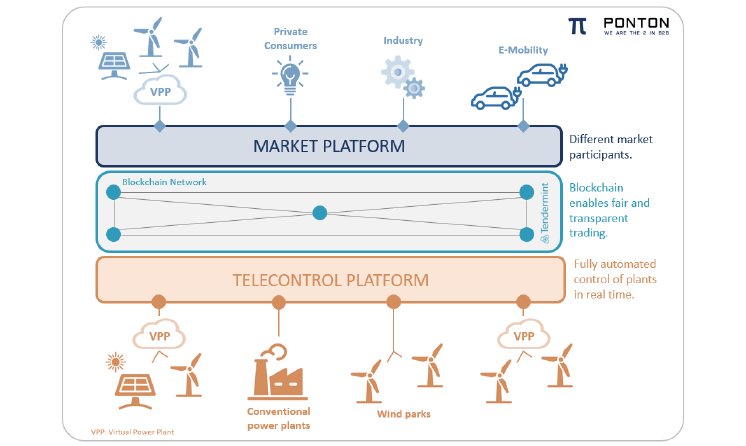
Various innovative use cases were successfully performed under real conditions, including short-term trades of flexibility, based on individual delivery intervals, between large industrial consumers such as TRIMET Aluminium SE, ArcelorMittal Hamburg GmbH and Aurubis AG [1]. Those producers need vast amounts of energy for their production processes and they occasionally offer excess energy which they can sell on a short-term basis. The NEW 4.0 energy trading platform “Energieplattform” enables monetization of flexibilities by selling power to consumers which have unexpected demand for additional energy. This enables a more efficient usage of regional flexibilities which are dormant in industrial processes. Other market driven scenarios during the field test involved municipal supplier: Stadtwerke Norderstedt delivered green excess power, produced by wind farms, to their retail clients and Stadtwerke Flensburg demonstrated sector coupling by connecting their power-to-heat plant to the “Energieplattform”.
For the first time, the actual generation and consumption of electricity was automatically adjusted only seconds after a trade occurred on the market platform, an important breakthrough towards allowing real-time deliveries in the longer run. Power trading on traditional intraday markets often ends half an hour before the delivery period occurs. It is difficult to forecast volatile, renewable energy production from sources such as wind and solar as well as excess energy from industrial processes which change often in the last minute. Reducing the time gap between trading and delivery leads to efficiency improvements.
In addition, the origin and green trait of the generated electricity is made transparent on the Energieplattform, a particular advantage of the underlying blockchain based solution. This can be done even when the generated electricity is changing hands multiple times before delivery and even when used across different energy sectors (e.g. power-to-heat).
The technology for the Energieplattform is based on different software components: PONTON has developed the decentralised marketplace which is based on the WRMHL blockchain framework (https://www.ponton.de/wrmhl/), while HAMBURG ENERGIE developed the telecontrol adapter, which enables real-time control of production and consumption installations based on trades between counterparties. Through an open API, the Energieplattform provides an interface which makes it easy to connect clients such as automated trading robots. The WRMHL framework, which itself is based on the open source blockchain technology Tendermint, (www.tendermint.com), allows for a very fast block time (1 sec) and supports high transaction throughput, so that larger order volumes can be processed that occur when using trading robots. The specific trading logic of the Energieplattform enables anonymous OTC trading of local energy without the need for an intermediary, all-in-all leading to reduced transaction costs.
The field test was recognised as a great success by the Germany ministry of Economic Affairs and Energy and as an important milestone on the road to the energy system of the future, bringing North Germany a step closer to going 100% renewable [2]. The NEW 4.0 project is supported by the state governments of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein as well as by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs (BMWI) as part of the SINTEG (Smart Energy Showcase) programme.
Learn more about the NEW 4.0 project and discuss further challenges in the context of energy transition at the upcoming E-World exhibition (11-13 February, Essen Germany). At its booth (hall 1 / Stand 1-318) PONTON will be presenting the NEW 4.0 project and further innovative solutions for market based flexibility management and B2B integration for efficient energy data exchange.
[1] 18.12. Hamburg Energie (in German) Erfolgreicher Test: Überschussstrom aus der Industrie nutzen
[2] 05.12. NEW 4.0 (in German) Wichtiger Meilenstein auf dem Weg zum Energiesystem der Zukunft Energiewendeprojekt NEW 4.0 führt erfolgreichen Feldtest durch
Further information about NEW 4.0 (in English):
https://www.haw-hamburg.de/english/research/energy-sustainability/cc4e/new-40.html